- Problem
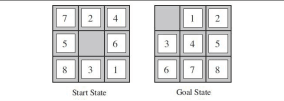
如图,通过A*算法求出最优解法
- Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include "math.h"
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int direction[][2] = {
{ 0, -1 },
{ 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0 },
{ -1, 0 }
}, maxCost = 30;
class node {
public:
node(int* begin=nullptr) : val(9, -1) {
init(begin);
}
void init(const int* begin) {
blackPos = -1;
fn = 0;
cost = 0;
path = "";
if (begin) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
val[i] = begin[i];
if (!val[i]) {
blackPos = i;
}
}
}
}
string toString() {
string str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
str += val[i] ? val[i] + '0' : ' ';
str += " ";
if ((i + 1) % 3 == 0) {
str += "\n";
}
}
return str;
}
bool equal(const node& target) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
if (val[i] != target.val[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int hn(const node& target) {
int dis = 0, sum = 9, index[9];
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
index[target.val[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
int value = val[i];
dis = abs(i / 3 - index[value] / 3) + abs(i % 3 - index[value] % 3);
sum += dis;
}
return cost + sum - 1;
}
string getPath() {
return path + "->\n" + toString();
}
node move(int i) {
int nextX = blackPos / 3 + direction[i][0],
nextY = blackPos % 3 + direction[i][1];
node next = *this;
next.cost = cost + 1;
next.path = getPath();
if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX > 2 || nextY > 2) {
next.cost = -1;
}
else {
next.blackPos = nextX * 3 + nextY;
next.val[blackPos] = next.val[next.blackPos];
next.val[next.blackPos] = 0;
}
return next;
}
vector<int> val;
int blackPos;
int cost;
int fn;
string path;
};
pair<int, string> search(const node &start, const node &target) {
std::vector<node> q;
unordered_map<string, int> closet;
q.push_back(start);
while (!q.empty()) {
node cur = q[0];
q.erase(q.begin());
if (cur.equal(target)) {
return make_pair(cur.cost, cur.getPath());
}
closet[cur.toString()] = cur.cost;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
node next = cur.move(i);
string key = next.toString();
if (next.cost < maxCost && next.cost != -1 && (closet.find(key) == closet.end() || closet[key] > next.cost)) {
next.fn = next.hn(target);
q.push_back(next);
}
}
sort(q.begin(), q.end(), [&](const node &a, const node &b) {
return a.fn < b.fn;
});
}
return make_pair(-1, "couldn't find");
}
int main() {
int a[9] = { 7, 2, 4, 5, 0, 6, 8, 3, 1 },
b[9] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
node start(a), end(b), randomMap = end;
/*
随机puzzle生成
srand(unsigned(time(0)));
int randomSize = rand() % 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < randomSize; i++) {
int j = rand() % 4;
node next = randomMap.move(j);
if (next.cost != -1) {
randomMap = next;
}
}
start = randomMap;
*/
start.cost = 0;
start.path = "";
cout << "from \n" << start.toString() << "to\n" << end.toString() << "cost ";
auto t = search(start, end);
cout << t.first << " steps\n" << t.second << endl;
return 0;
}
Result
备注
关于上面代码中的maxCost变量,这主要是我观察了多个puzzle的搜索结果,发现他们的步骤都小于30,于是进行了大胆的猜想,正确性未知。
不过,由此想到了迭代加深算法,我们可以把每次被maxCost砍掉的节点保存下来,然后如果在当前maxCost下未找到结果,则maxCost加大,再从这些被砍掉的节点处重新开始关于 h(n) 为什么是cost + sum。
若 h(n) 只有sum来决定,则会出现这种情况,当cost对结果的影响超过sum时,将因为缺失对cost的判断而导致求出的解有可能不是最优解。